
François de Bellefon - Customer Success Manager
Continuous flow process machines facilitate the optimization of operational processes and improve overall performance. This uninterrupted sequence of steps in the production chain reduces wait times and even stops and aims to eliminate waste. However the wasteful energy consumption of continuous flow process machines becomes a major problem. Since production is dependent on the flow of matter, information or human factors, it is actually slowed down when these flows are not perfectly synchronized.
The production machines are ready to produce but the upstream feeding defects where expectations of any kind (related to the human or the machine) cause significant losses and unjustified overconsumption of electricity or pneumatic.
In the current context, where the objective of industrialists is to reduce energy consumption by at least 10%, it is necessary to find a solution.
The start-and-stop technology used in the automotive sector to reduce fuel consumption and protect the environment is unfortunately not yet adapted to production machines. So how do we do it?
The collection and analysis of production data make it possible to identify micro/macro stops (duration, frequency, causes) and situations where the machine could have been stopped following a state of non-production.
For example, we carried out the exercise at one of our customers with complete industrial packaging production lines.
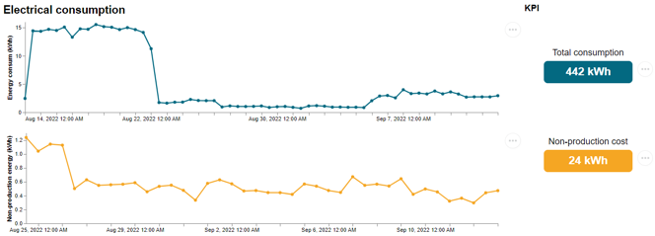
The graphs generated by connected machines show the power consumption according to the state of the machine.

Over the last 30 days, electricity consumption in a non-production state is 24kWh. This can be observed on a saturation or defusing phase during which the machine remains on. A leak in the system can also lead to this type of overconsumption.
The data offer the opportunity for manufacturers to identify the levers of action to control energy expenditures. In particular, they can understand which stage of the production chain leads to unnecessary energy consumption and thus intervene quickly with an appropriate action plan.
With this solution, our customer’s energy consumption could be reduced by 5%.
Discover our applications:
Related News
